You can here know about the calcium valence electrons to boost your chemistry knowledge. The article will disclose the various electron valence information of elements. Well, just like the other elements in chemistry Calcium is also a chemical element. The chemical comes from the family of Alkaline earth metals.
- Flerovium Valence Electrons
- Helium Valence Electrons
- Plutonium Valence Electrons
- Lithium Valence Electrons
- Mercury Valence electrons
- Americium Valence Electrons
- Neptunium Valence Electrons
- Oxygen Valence Electrons
- Sodium Valence Electrons
- Magnesium Valence Electrons
- Bismuth Valence electrons
- Aluminum Valence Electrons
- Silicon Valence Electrons
- Beryllium Valence Electrons
- Livermorium Valence Electrons
- Fluorine Valence Electrons
- Radon Valence electrons
- Carbon Valence Electrons
- Xenon Valence Electrons
- Neon Valence Electrons
- Tennessine Valence Electrons
- Antimony Valence Electrons
- Radium Valence Electrons
- Oganesson Valence Electrons
- Iodine Valence Electrons
- Lead Valence electrons
- Tellurium Valence Electrons
- Boron Valence Electrons
- Gold Valence Electrons
- Nobelium Valence Electrons
- Neon Valence Electrons
- Hydrogen Valence Electrons
It’s a very reactive element since it easily reacts in the exposure of oxygen. In appearance, Calcium looks like a grey, silver puffy substance. Calcium is one of those elements which we can easily find in abundance within the earth. Moreover, calcium is also a significant part of the human body structure.
You can find calcium as the core component of human bones etc. It’s one of the most vital naturally occurring chemical elements in human bodies.
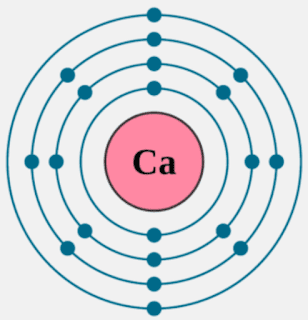
Calcium Valence Electrons Dot Diagram
You can definitely refer to the Lewis dot diagram to explore the electron valence of Calcium. The diagram represents the valence electron of Calcium atoms and molecules.
The diagram helps in understanding the bonding structure of atoms and molecules for the valence electrons. We advise you to go through the Dot diagram of Calcium to get in-depth insight.
Calcium chloride exists as dihydrate (CaCl2x2h20). It has 2 valence. According to the definition of valence: 'valence, combining capacity of an atom expressed as the number of single bonds the atom can form or the number of electrons an element gives up or accepts when reacting to form a. You can here know about the calcium valence electrons to boost your chemistry knowledge. The article will disclose the various electron valence information of elements. Well, just like the other elements in chemistry Calcium is also a chemical ele. .For atoms with LESS than 4valence electrons, they’re going to lose/give upelectrons to form positive cations.For atoms with MORE than 4valence electrons, they’re going to gain/stealelectrons to form negative anions.For atoms with 4 valence electrons, it can go either way.For atoms with 8 valence electrons, there is no change.
Valency of Calcium
The valency of Calcium is always 2+ with its electron configuration as 2,8,8,2. So, it contains 2 electrons in its outer shell. So, in other words, Calcium can either gain or lose 2 electrons. As per the octet rule, calcium will gain stability by gaining or losing 2 electrons.
The valency of a chemical element is an important characteristic of the element. This is therefore the ideal property of the given element to attain stability.
How many valence electrons does Calcium have?
Furthermore, are generally two rules to figure out the valency of an element. The first rule is the octet rule while the second rule is the duplet rule. You can apply either of the rules to calculate the valency of calcium. Moreover, you can also refer the periodic table to determine the correct valency of Calcium.
In physical engineering and chemical science, there are mainly two types of chemical bonds. These are Ionic Bonds and Covalent bonds. In this exclusive article, I am going to explain the definition of Ionic Bond.
However, I will still clear some air regarding the basic difference between covalent and ionic bonds. See, a covalent bond is sharing of electrons between two atoms. On the other hand, an ionic bond is a permanent transfer of valence electrons between two atoms.
Just to let you know, apart from ionic and covalent bonds, there are two more types of chemical bonds. These are hydrogen bonds and polar bonds.
What is Ionic Bond?
By definition, an Ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs due to the permanent transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another.
The atom that permanently loses electrons becomes a cation i.e positively charged ion. On the other hand, the atom that gains electrons becomes an anion i.e negatively charged ion. That’s why an ionic bond is also known electrovalent bond.
Editor’s Choice: Covalent Bond – Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
To summarise, by definition, an ionic bond or simply electrovalent bond is a type of chemical bond that forms due to the electrostatic attraction between the positively charges cation and negatively charged anion.
Role of Electronegativity in Ionic Bond
For an ionic bond to form, there has to be a very large difference in the value of electronegativity between the participating atoms. As a result, the formation of ions takes place in ionic bonding.
And, for that to happen, ionic bonding can only form between metals and non-metals. To summarise, one can also say that two metals can never form an ionic bond. The same goes with non-metals too.
To put it differently, if we take two metals or non-metals, and try to form an ionic bond, it won’t form. WHY? Because there won’t be enough difference in the value of electronegativity of the participating atoms to form an ionic bond.
Properties of Ionic Bond
There are so many properties of ionic bonds. Some of them are listed below:
- By definition, Ionic bond is non-directional in nature.
- Ionic compounds are soluble in water and polar solvents.
- Ionic compounds are insoluble in non-polar solvents.
- They have the highest melting and boiling points.
- They show good electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Ionic bonds or electrovalent bonds are the strongest among all types of bonds.
- They form due to the permanent transfer of electrons, etc.
Examples of Ionic Bond
If you think you can’t relate to Ionic bond examples in everyday life. Well, here is your chance to think again!
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
A typical example of an ionic bond is the Sodium Chloride molecule. A molecule of Sodium Chloride (NaCL) consists of one Sodium and one chlorine atom.
Calcium Number Of Valence Electrons
Sodium has one valence electron in its outermost shell. On the other hand, Chlorine has seven valence electrons in its outermost shell.
Therefore, when one atom of sodium and one atom of Chlorine combines to form an ionic bond, in order to complete its Octet, Sodium will donate its lone electron. Hence becomes sodium ions (Na+).
On the other hand, just because chlorine is more electronegative than sodium, it will accept the donated electron. Hence becomes chloride ions (Cl–). By this, two atoms combine to form an ionic bond-based compound i.e Sodium Chloride (NaCL).
Potassium Oxide (K2O)
The next example of an ionic bond is the Potassium Oxide molecule. A molecule of Potassium Oxide (K2O) consists of two potassium and one oxygen atom. Potassium has one valence electron in its outermost shell.
On the other hand, oxygen has six valence electrons in its outermost shell. Therefore, when two atoms of Potassium and one atom of oxygen combine to form an ionic bond, in order to complete its Octet, both of the Potassium atoms will donate their lone electron.
Hence becomes a Potassium ion (K+). On the other hand, just because Oxygen is more electronegative than Potassium, it will accept both of the donated electrons. Hence becomes oxide ion (O-).
By this, two atoms of potassium and one atom of oxygen combine to form an ionic bond-based compound i.e Potassium Oxide (K2O). Not to mention, just because there are two potassium atoms, the molecule of potassium oxide has two ionic bonds.
Calcium Chloride (CaCL2)
The last one in my list of examples of an ionic bond or electrovalent bond is the Calcium Chloride molecule. A molecule of Calcium chloride (CaCL2) consists of one calcium and two chlorine atoms. Calcium has two valence electrons in its outermost shell.
Similarly, chlorine has seven. Therefore, when one atom of calcium and two atoms of chlorine combine to form an ionic bond, in order to complete its Octet, the calcium atom will donate its two electrons. Hence becomes a calcium ion (Ca+).
On the other hand, just because chlorine is more electronegative than Calcium, both of the chlorine atoms will accept one each of the donated electrons. Hence becomes a chloride ion (Cl–).
By this, one atom of calcium and two atoms of chlorine combine to form an ionic bond-based molecule i.e Calcium Chloride (CaCL2). Not to mention, just because there are two chlorine atoms, the molecule of calcium chloride has two ionic bonds.
Uses of Ionic Compounds
Compounds that form due to ionic bonding is known as Ionic Compounds. Again, If you think you can’t relate to the uses of ionic compounds in everyday life. Well, here is your chance to think again!
List Of Valence Electrons For Each Element
- Sodium chloride as table salt
- De-icing of roads after snowfall
- As a preservative in cold storage
- Water fluoridation, etc.
Valence Electrons In Calcium Iodide
At last, that’s it for this post. If you like this article, share it if you like, like it if you share it. You can also find us on Mix,Twitter,Pinterest, and Facebook.
